COMPUTER LANGUAGES
COMPUTER
LANGUAGES
Languages
are a means of communication. Normally people interact with each other through
a language. On the same pattern, communication with computers is carried out
through a language. This language is understood both by user and the machine.
Just as every language like English, Hindi has its grammatical rules; every
computer language is bound by rules known as SYNTAX of that language. The user
is bound by that syntax while communicating with the computer system.
Computer Languages
Computer
languages are broadly classified as:
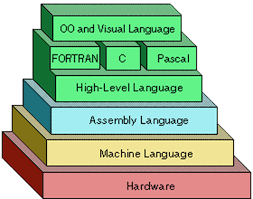
1. Low Level Language:
The
term low level means closeness to the way in which machine understand. The low
level languages are:
a. Machine Language:
This is the language (in the form of 0’s and 1’s, called binary
Numbers)
understood directly by the computer. It is machine dependent. It is difficult
to learn and even more difficult to write programs.
b. Assembly Language: This
is the language where the machine codes comprising of 0’s and 1’s are substituted
by symbolic codes (called mnemonics)
to improve their understanding. It is the first step to improve programming
structure. Assembly language programming is simpler and less time consuming
than machine level programming, it is easier to locate and correct errors in
assembly language than in machine language programs. It is also machine
dependent. Programmers must have knowledge of the machine on which the program
will run.
2. High
Level Language
You know
that low level language requires extensive knowledge of the hardware since it
is machine dependent. To overcome the limitation, high level language has been
evolved which uses normal English like, easy to understand statements to solve
any problem. Higher level languages are computer independent and programming
becomes quite easy and simple.
Various
high level languages are given below:
BASIC (Beginners All Purpose
Symbolic Instruction Code): It is widely
used, easy to learn general purpose language. Mainly used in microcomputers in
earlier days.
COBOL (Common Business Oriented
language): A standardized language used for
commercial applications.
FORTRAN (Formula Translation):
Developed for solving mathematical and scientific problems. One of the most popular
languages among scientific community.
C: Structured
Programming Language used for all purpose such as scientific application,
commercial application, developing games etc.
C++: Popular
object oriented programming language, used for general purpose.
COMPILER AND ASSEMBLER
As
you know that High Level language is machine independent and assembly language
though it is machine dependent yet mnemonics that
are being used to represent instructions are not directly understandable by
machine. Hence to make the machine understand the instructions provided by both
the languages, Compiler and Assembler are required to convert these instructions
into machine language. The software (set of programs) that reads a program
written in high level language and translates it into an equivalent program in machine
language is called as Compiler. The program
written by the programmer in high level language is called source
program and the program generated by the compiler
after translation is called as object program.
Compiler
The
software (set of programs) that reads a program written in assembly language
and translates it into an equivalent program in machine language is called as Assembler.
Assembler.



Good Jobs
ReplyDeletenice
ReplyDelete